Heritage is described by the Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment (DAWE) as:
“All the things that makeup Australia’s identity – our spirit and ingenuity, our historic buildings, and our unique, living landscape. Our heritage is a legacy from our past, a living, an integral part of life today, and the stories and places we pass on to future generations”.
Heritage sites are found all over Australia and can be broadly classified into three categories; Aboriginal Heritage, Non-Aboriginal (European) Heritage or Natural Heritage. Being able to identify the location of heritage sites is extremely important when planning projects to ensure there is no impact on sites, artefacts or cultural values. In Western Australia, heritage is protected under the Heritage Act 2018 and the Aboriginal Heritage Act 1972 (currently under review), and Nationally by the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 (EPBC Act).
This Insight explores some of the resources, lists and databases available to assist with identifying declared heritage sites in Western Australia. For more information on Western Australian Heritage, please refer to our previous Insight, ‘Western Australian Heritage’.
Aboriginal Heritage
Under section 38 of the Aboriginal Heritage Act 1972 (AHA), a register of protected Aboriginal areas and cultural material must be maintained. Registered Aboriginal sites, other heritage places and heritage surveys can be accessed through the Aboriginal Heritage Inquiry System (AHIS). The AHIS was developed and is maintained by the Department of Planning, Lands and Heritage (DPLH) and is free to use a public data source that provides details about Aboriginal heritage places (DPLH, 2020a), such as:
- The location and extent of each place (the exact location of some pleases may be restricted or hidden by a buffer);
- The assessment status of each place under the AHA; and
- Any access restrictions the place may have or additional information held by DPLH.
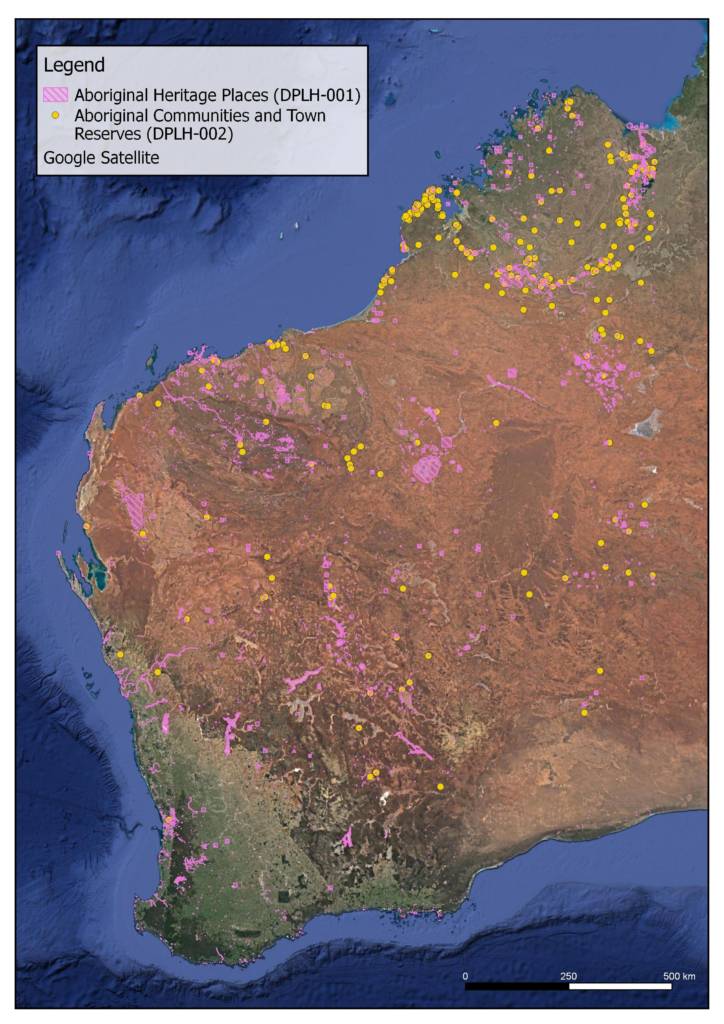
The database can be used to search for Aboriginal heritage sites within WA using area restrictions, boundaries (such as mining tenure or shires) or spatial data. The AHIS can be accessed here. It is important to note that the AHA makes it an offence to damage an Aboriginal place or object without approval, whether it is on the register or not (National Trust, 2020). Therefore, it is recommended you engage a suitably qualified professional prior to commencing a project to assist with heritage identification and to identify your requirements.
DPLH also have a number of spatial layers available for download or to link to geographic information systems (GIS), available through Data WA. Datasets include Aboriginal Heritage Places (DPLH-001), Survey Areas (DPLH-080) and Settlements (DPLH-011) amongst others. While these layers can only be downloaded with a subscription, they can be viewed for free using the AHIS or Locate database.
Locate is a public map viewer maintained by Landgate that showcases the Shared Location Information Platform (SLIP) and Western Australia’s location-based information (Landgate, 2019).
Non-Aboriginal Heritage
The DPLH maintains the State Register of Heritage Places. The State Register is a statutory list of places that represent Western Australia’s history and development. The State Register includes listings pertaining to buildings, structures, gardens, cemeteries, memorials, landscapes and archaeological sites. Entry in the Register is reserved for places of State cultural heritage significance and is the highest recognition afforded at the State level (DPLH, 2020b). The Heritage Council WA has published a list of State Registered Places in a Registration Report current as of June 2020.

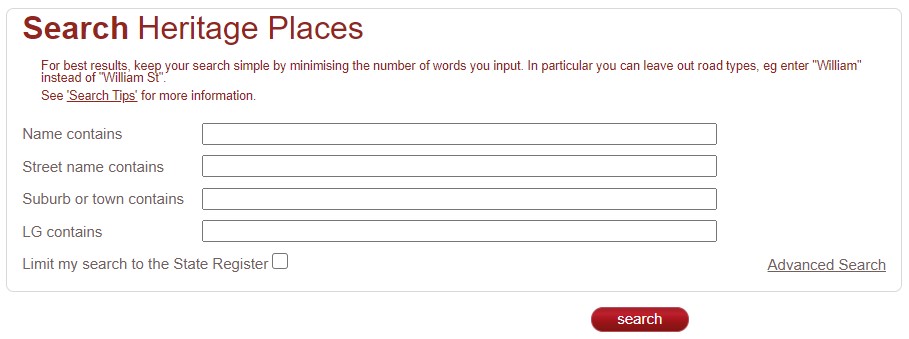
Heritage places can also be accessed or located using inHerit. inHerit is a free tool to use public online database maintained by DPLH that contains information about heritage places and listings in Western Australia. Searches in inHerit are a little more restricted than some of the other heritage databases. Searches are either very specific or broad. In that boundaries, maps or spatial data cannot be used to dictate search areas, rather this is done using physical addresses, names, place numbers, suburbs or towns. Once a site has been located, the information listed below is available:
- Statutory Heritage Listings;
- Heritage Council Decisions and Deliberations;
- Other Heritage Listings and Surveys;
- Images, history and broad descriptions.
DAWE maintains a Heritage Database that can be used to search for National, World, and Commonwealth Heritage and national estates and overseas places of historical significance to Australians. The search functionality is similar to that of inHerit; however, it also allows for searches to be conducted using coordinates to dictate search areas. Information that can be accessed through the site includes a Statement of Significance, descriptions, history, conditions and location.
DAWE also maintains the database for Underwater cultural heritage. Australia protects its shipwrecks, sunken aircraft and other types of underwater heritage and their associated artefacts through the Underwater Cultural Heritage Act 2018 (DAWE, 2020). Please refer to our previous InSight ‘Australia’s Underwater Cultural Heritage’ for more information on Underwater cultural heritage. The Australasian Underwater Cultural Heritage Database contains historical and environmental information about shipwrecks, sunken aircraft, and other underwater heritage sites located in the Oceania and Southeast Asian regions. This database also includes the records of artefacts that originate from these sites (DAWE, 2020).

Natural Heritage
Many natural sites and landforms are protected by state or national legislation and can be identified using the inHerit database or DAWE search tools. Specific databases and search tools are also available for natural heritage; however, it is important to ensure the validity and accuracy of the site you are using, as many are maintained by private companies and organisations.
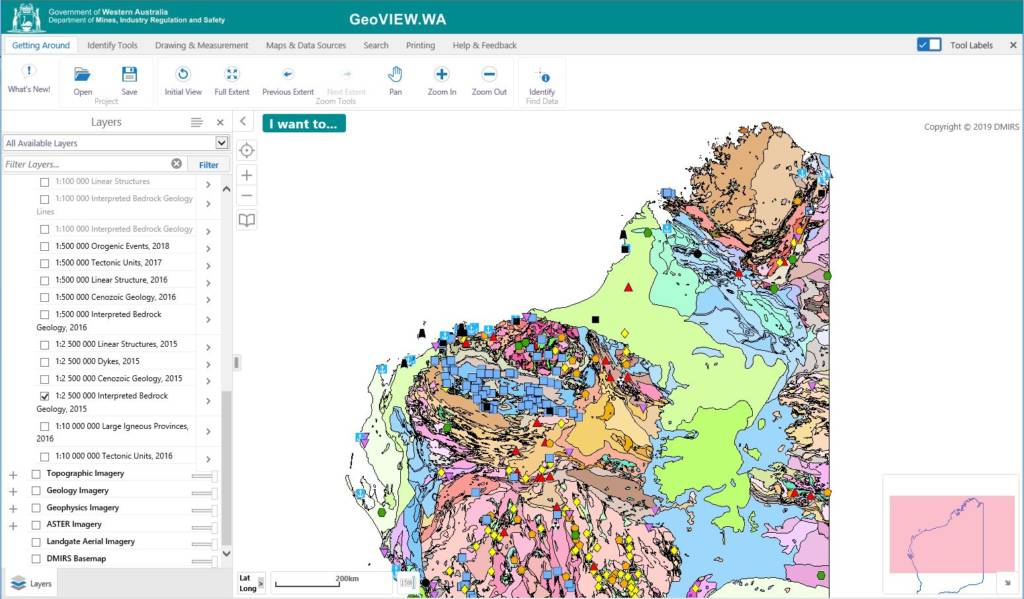
The Geological Survey of Western Australia maintains a state register of geoheritage sites (currently 150 sites). Geoheritage is about managing, preserving and protecting exceptional geological features. A geoheritage site has geological features considered to be unique and of outstanding scientific and educational value within Western Australia (DMIRS, 2020). GeoVIEW.WA is an online GIS-based mapping tool that allows users to view, query, and map various geology, resources and related datasets. Geoheritage sites can be viewed by selecting the ‘GeoHeritage Sites’ category located under the ‘Special Category Lands’ tab. The site also gives you the option of downloading data.
Most of the heritage databases discussed in this InSight offer a variety of applications and can be used to locate a number of items. It is important to remember, as with any database, to ensure the information you are using is appropriate, accurate and valid. Our team at Integrate Sustainability utilises a number of these sites and databases to assist clients with heritage matters; while ensuring we remain updated with legislative changes, database content and other resources.
ISPL also works with specialist archaeologists and heritage experts to coordinate heritage surveys across Australia. We have experience providing a range of services to support exploration and mining applications and develop procedures and plans to assist operations with managing heritage sites’ preservation. If you need assistance with heritage matters or connecting with your local community, please contacts us via enquires@integratesustainability.com.au or phone 9468 0338.
References
DAWE. (2020, July). Underwater cultural heritage. Retrieved from Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment: http://www.environment.gov.au/heritage/underwater-heritage
DMIRS. (2020, August). Geoheritage. Retrieved from Department of Mines, Industry Regulation and Safety: http://www.dmp.wa.gov.au/Geological-Survey/Geoheritage-1412.aspx
DPLH. (2020a). Aboriginal heritage inquiry system. Retrieved from Government of Western Australia; Department of Planning Lands and Heritage: https://www.dplh.wa.gov.au/ahis
DPLH. (2020b, August). The State Register and other heritage listings. Retrieved from Department of Planning, Lands and Heritage: https://www.dplh.wa.gov.au/about-inherit
Heritage Council of WA. (2020). State Register of Heritage Places Current Registration Report. Government of Western Australia. Retrieved from https://www.dplh.wa.gov.au/getmedia/ac785512-919e-4720-98dd-3ee49ecc0607/HH-State-Register-of-Heritage-Places-June-2020
Landgate. (2019). Locate. Retrieved from Landgate, Government of Western Australia: https://www0.landgate.wa.gov.au/maps-and-imagery/interactive-maps/locate
National Trust. (2020). Heritage Register WA. Retrieved from National Trust WA: https://www.nationaltrust.org.au/services/Heritage-Register-wa/

